Introduction
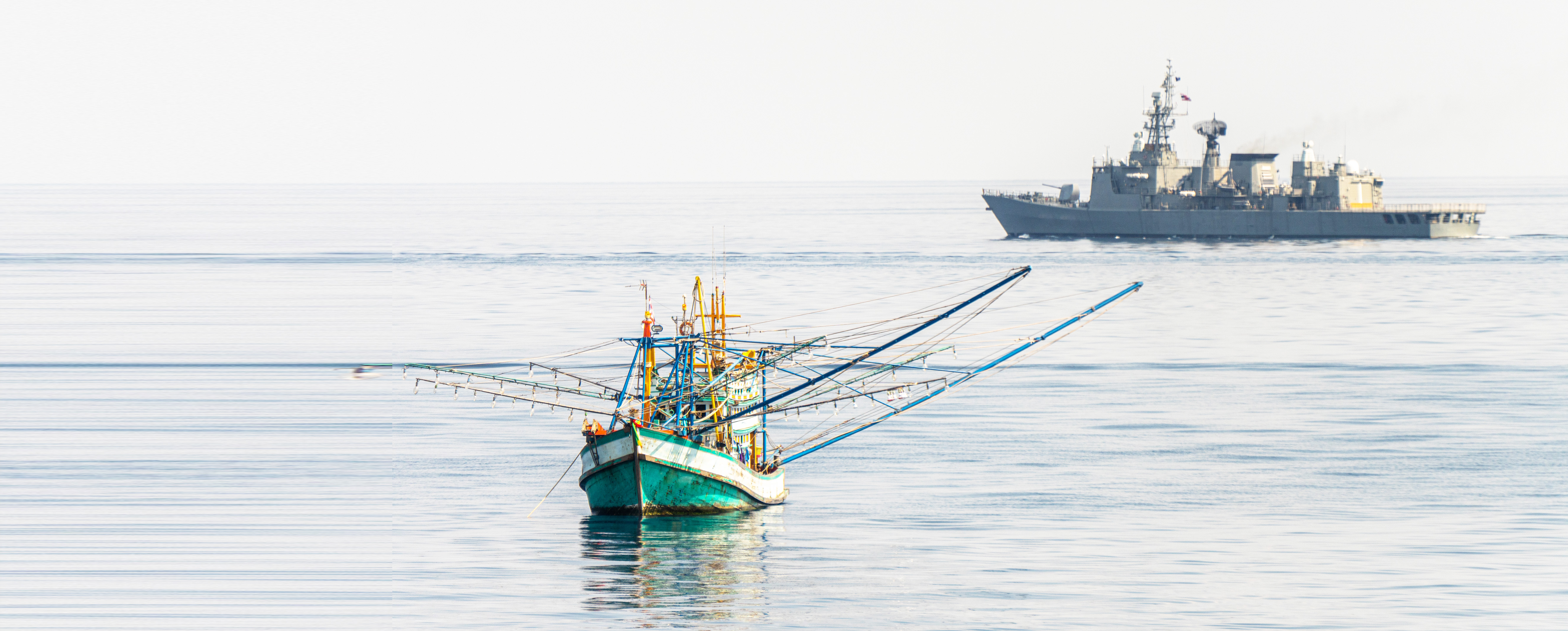
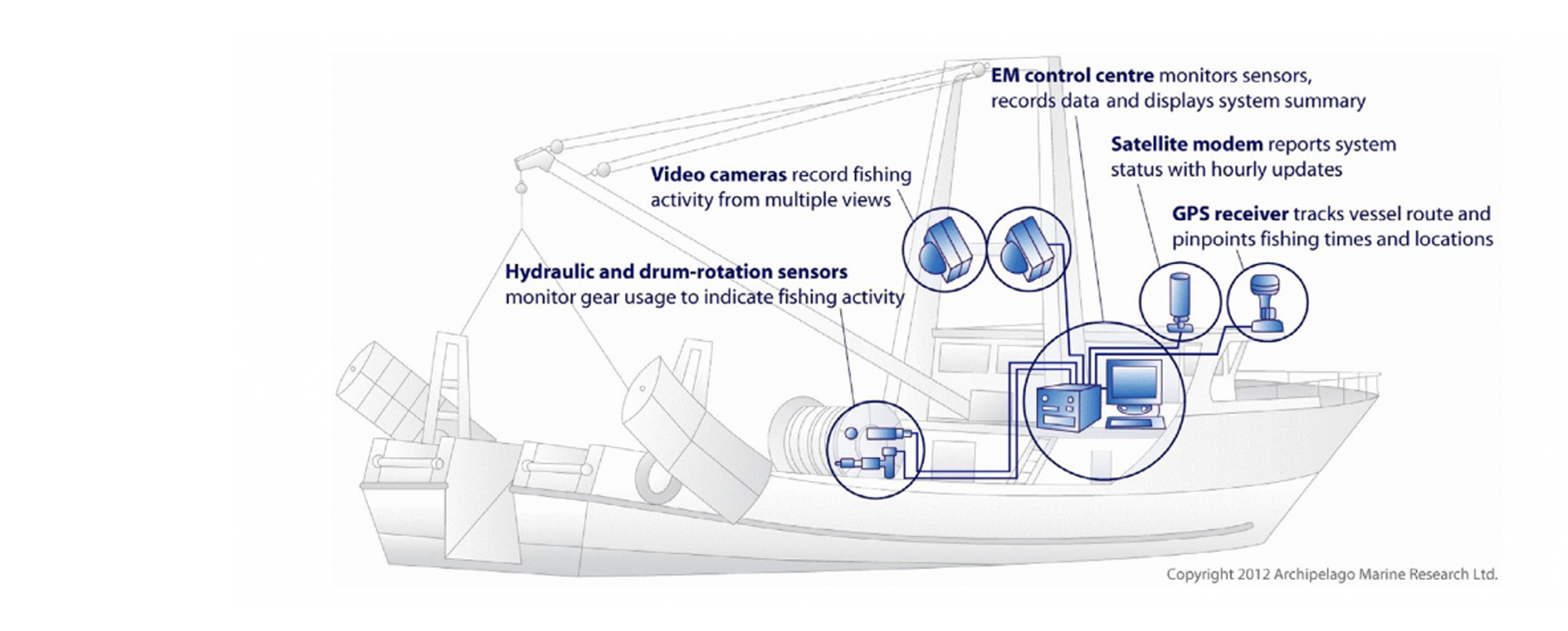
Illegal, Unreported and Unregulated (IUU) fishing is a major international issue affecting the sustainability of fisheries resources, both within national jurisdictions and on the high seas. This illegal practice undermines sustainable fisheries management by operating outside legal frameworks, leading to the depletion of fish stocks and hindering sustainability efforts. Estimates suggest yearly global losses of between 11 million and 26 million tonnes of catch, valued at USD 10–23.5 billion, while the broader economic ramifications, including income losses and tax revenue declines, can range from USD 34 billion to USD 67 billion . Southeast Asian countries face increasing pressure on their fisheries resources due to IUU fishing, often linked to insufficient management and lack of monitoring, control, and surveillance (MCS). These countries must prioritize preventive measures, such as regulating fishing vessels, addressing overcapacity, and implementing effective rights-based fisheries systems. IUU fishing undermines national and regional conservation efforts, putting responsible fishers at a disadvantage and requiring urgent, transparent action.
SEAFDEC together with the Bay of Bengal Programme Inter-Governmental Organization (BOBP-IGO) and International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), will be executing the Sustainable management of fisheries, marine living resources, and their habitats in the Bay of Bengal region for the benefit of coastal states and communities (BOBLME II) project, an initiative of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the Global Environment Facility (GEF), being implemented in seven countries, comprising Bangladesh, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Maldives, Sri Lanka, and Thailand. The project’s main objective is to contribute to the sustainable management of fisheries, marine living resources, and their habitats in the Bay of Bengal region, to reduce environmental stress; and to improve environmental status for the benefit of coastal states and communities. This will be accomplished through five interlinked components: 1) Sustainable Management of Fisheries, 2) Restoration and conservation of critical marine habitats and conservation of biodiversity, 3) Management of coastal and marine pollution to improve ecosystem health, 4) Improved livelihoods and enhanced resilience of the BOBLME, 5) Regional mechanism for planning, coordination and monitoring of the BOBLME. SEAFDEC as an Executing Agency (EA) will be leading the Southeast Asia sub-regional coordination, technical advice, and capacity building on related fishery issues under components 1, 3, and 5 which are being implemented from 2024 to 2028.
Read More



 The Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center (SEAFDEC) is an autonomous inter-governmental body established in 1967. The mission of SEAFDEC considered and adopted by the Special Meeting of the SEAFDEC Council 2017 is “To promote and facilitate concerted actions among the Member Countries to ensure the sustainability of fisheries and aquaculture in Southeast Asia.”
The Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center (SEAFDEC) is an autonomous inter-governmental body established in 1967. The mission of SEAFDEC considered and adopted by the Special Meeting of the SEAFDEC Council 2017 is “To promote and facilitate concerted actions among the Member Countries to ensure the sustainability of fisheries and aquaculture in Southeast Asia.” 


